Protecting Human Rights
CENTRAL AMERICA MONITOR:
EVALUATING PROGRESS
Central America’s Northern Triangle region is struggling with violence, corruption and impunity.
Scroll for the key findings or to find links to download the full reports under each area of progress.
Evaluating progress in Central America
As Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras struggle with high levels of violence and insecurity, systemic corruption, and widespread impunity, it’s critical that we find ways to assess how the policies and strategies being implemented in the region are contributing to the strengthening of the rule of law, improving transparency and accountability, and to reducing violence and insecurity. Using a comprehensive series of indicators, the Central American Monitor aims to measure progress and identify trends over time in eight key areas directly relevant to rule of law and security, thus providing critical information that can inform policies and strategic investments in the region.
The Washington Office on Latin America (WOLA), the Myrna Mack Foundation (FMM) of Guatemala, the University Institute for Public Opinion (Iudop) of the José Simeón Cañas Central American University (UCA) of El Salvador, the University Institute on Democracy, Peace and Security (IUDPAS) of the National Autonomous University of Honduras (UNAH) have developed a series of qualitative and quantitative indicators to evaluate progress in Central America in eight key areas.
Protecting Human Rights
Areas of progress
1.
Investigation and Conviction of Human Rights Violations
Across all categories of human rights violations, the prevailing trend is the low proportion of cases that are prosecuted, and even smaller proportions that end in conviction. Between 2014 and 2017, the Public Prosecutor’s Office's most frequently initiated cases involve unlawful entry, deprivation of liberty and unlawful searches and investigations. Of these three crimes, only 8.5 percent of the cases were taken to court.
Regarding cases of crimes against humanity, twice the number of cases were initiated for torture than those initiated for forced disappearances, and only a fifth of the crimes involving torture or forced disappearances were ever prosecuted.
During the 2014-2017 period, the information compiled points to various instances of extrajudicial executions. The increase in confrontations between police and gang members has resulted in a greater proportion of deaths at the hands of the police.
However, in the case of El Salvador, extrajudicial execution has not been defined in the criminal code. Consequently, the Public Prosecutor’s Office does not provide specific data on the alleged commission of extrajudicial executions.
An analysis of press articles carried out by Iudop identified 111 events in 2016 that displayed characteristics of alleged extrajudicial executions, in which 278 fatalities were reported. Of these, 50.4 percent were deaths from confrontations between alleged gang members and police and members of the army, 26.1 percent from confrontations between combined forces and alleged gang members, and 21.6 percent deaths caused by alleged death squads.
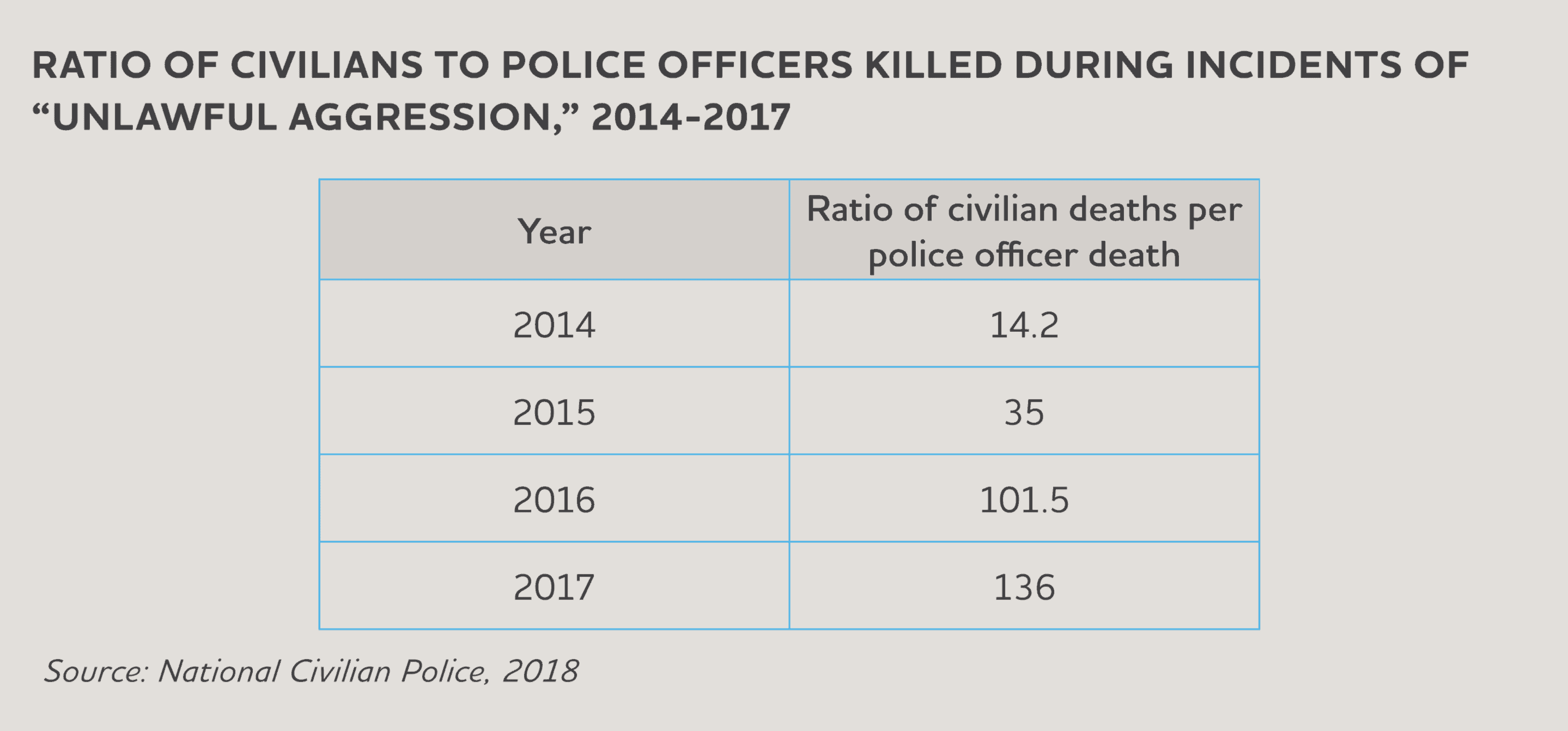
The chart below shows the ratio of civilians to police officers killed during incidents of “unlawful aggression” from 2014 to 2017 recorded by the University Observatory for Human Rights.
Protecting Human Rights
Areas of progress
2.
Protection Mechanisms
The appropriate Salvadoran institutions- such as the Public Prosecutor’s Office and the Human Rights Ombudsman- lack an official corresponding registry as well as special units charged with handling rights violations of human rights defenders. They also lack specific protocols and guidelines to respond to these kinds of violations.
Because El Salvador lacks a national protection mechanism to guarantee the safety of human rights defenders, when a violation against defenders occurs, the incidents are registered and treated like common crimes. This results in an extremely low level of effectiveness in responding to complaints filed by defenders.
Because El Salvador lacks a national protection mechanism to guarantee the safety of human rights defenders, when a violation against defenders occurs, the incidents are registered and treated like common crimes. This results in an extremely low level of effectiveness in responding to complaints filed by defenders.
Protecting Human Rights
Areas of progress
3.
Hate Speech
The Monitor was unable to find quantitative data on attacks and defamation campaigns against defenders. According to data from secondary sources, members of the LGBTI community have faced violence by state agents, criminal groups and society in general.
Youth defenders have been victims of harassment and stigmatization by state security forces, while indigenous communities and environmental defenders have been the target of intimidation and harassment by sectors involved in the exploitation of natural resources.
Youth defenders have been victims of harassment and stigmatization by state security forces, while indigenous communities and environmental defenders have been the target of intimidation and harassment by sectors involved in the exploitation of natural resources.
GLOSSARY
The Washington Office on Latin America (WOLA), the Myrna Mack Foundation (FMM) of Guatemala, the University Institute for Public Opinion (Iudop) of the José Simeón Cañas Central American University (UCA) of El Salvador, the University Institute on Democracy, Peace and Security (IUDPAS) of the National Autonomous University of Honduras (UNAH) have developed a series of indicators to assess the progress in Central America in eight key areas. That progress will reflect both the commitment of Central American governments and the effectiveness of international assistance. The indicators include a combination of quantitative data and qualitative analysis in order to gain a more in-depth understanding of the changes taking place in each country. Data sources include official documents and statistics, surveys, interviews, and reviews of existing laws and regulations that will be systematically compiled.
WOLA, the Myrna Mack Foundation, Iudop, and IUDPAS developed these indicators in a months-long process that included review of international standards, consultation with experts, and consensus among all partners about the key issues to address.
Our goal is to provide an instrument that can help identify the areas of progress and opportunities for improvement shortfalls for of the policies and strategies being implemented on the ground in a form that is useful for policymakers, donors, academics, and the public. At the same time, we hope to provide analysis that can contribute to the evaluation of trends over time both within and between the countries of the Northern Triangle.
1
Strengthening the Capacity and Independence of Justice Systems
Capacity of the Justice System: Number of criminal justice officials, geographical coverage, workload, effectiveness, and public trust.
Internal Independence: Existence and implementation of a public, merit-based selection process free from external influence, a results-based evaluation system, and an effective disciplinary system.
External Independence: Size of budget allocated for the judicial sector and implementation of national and international protection measures for justice officials.
2
Cooperation with Anti-Impunity Commissions
Political Will and Level of Collaboration: Commitment of the state to collaborate and enable the work of the CICIG in Guatemala and the MACCIH in Honduras, demonstrated by the progress of emblematic cases, the approval of legislative reforms, and support for domestic counterparts working with these commissions.
3
Combating Corruption
Level of Public Trust: Degree of public trust in state institutions involved in efforts to prevent, identify, investigate, and punish corruption.
Scope and Implementation of Legislation to Combat Corruption: Classification of new crimes in criminal codes and reforms of existing anti-corruption laws to adhere to international standards.
Advancements in Criminal Investigations: Number of corruption cases filed, prosecuted, and resolved, as well as the progress made in emblematic cases.
Functioning of Oversight Bodies: Existence and capacity of external oversight bodies or agencies to combat corruption.
4
Tackling Violence and Organized Crime
Capacity Building: Existence and functioning of specialized anti-organized crime units, application of scientific and technical investigative methods, and functioning of judges or tribunals dedicated to the prosecution of organized crime
Advances in Criminal Investigations: The number of organized crime-related cases filed, prosecuted, and resolved, as well as the progress made in emblematic cases.
Crime Reduction: Convictions for homicides, extortion, and against criminal networks, as well as a reduction in serious and violent crimes.
5
Strengthening Civilian Police Forces
Functioning of Police Career Systems: Existence and effectiveness of police recruitment and promotion mechanisms, training processes, and disciplinary systems, as well as the structure of police bodies.
Allocation and Use of Budgetary Resources: Allocation and effective use of public funds and percentage designated for the wellbeing of members of the civilian police forces.
Community Relations: Public trust in the police, police-community relations, and relations with indigenous authorities.
6
Limiting the Role of the Armed Forces in Public Security Activities
Development and Implementation of a Concrete Plan: The design and implementation of a publicly accessible and verifiable plan with goals, timelines, activities, and clearly established indicators; repeal of legal norms authorizing participation of armed forces in public security, and access to information regarding payroll and assigned resources.
Conduct of Military Forces: Complaints, accusations, and sentences regarding human rights violations perpetrated by members of the armed forces and the level of public trust in the armed forces.
7
Protecting Human Rights
Investigation and Conviction of Human Rights Violations: Existence and functioning of specialized investigative units, number of complaints, prosecutions, and convictions, handling of emblematic cases, and degree of security forces’ collaboration with investigations.
Protection Mechanisms: Structure and functioning of domestic protection mechanisms and implementation of international protection measures for human rights defenders who have been victims of attacks or threats.
Hate Speech: Analysis of attacks and smear or defamation campaigns against human rights defenders.
8
Improving Transparency
Scope and Implementation of the ‘Law of Access to Public Information’: Type of information categorized as restricted or of limited access, period of classification, availability and quality of statistics related to security and justice, information requests granted and denied, and related fees.
Budget and Spending Transparency: Access to public information on budget allocations and spending on security, justice, and defense.
Disclosure of Public Officials’ Statement of Assets: Level of official compliance with disclosure norms, and the degree to which such statements are made available to the public.
METHODOLOGY
The Central America Monitor is based on the premise that accurate, objective, and complete data and information are necessary to reduce the high levels of violence and insecurity, and establish rule of law and governance in a democratic state. This will allow efforts to move beyond abstract discussions of reform to specific measures of change.
The Monitor is based on a series of more than 100 quantitative and qualitative indicators that allow a more profound level of analysis of the successes or setbacks made in eight key areas in each of the three countries. More than a comprehensive list, the indicators seek to identify a way to examine and assess the level of progress of the three countries in strengthening the rule of law and democratic institutions. The indicators seek to identify the main challenges in each of the selected areas and examine how institutions are (or are not) being strengthened over time. The Monitor uses information from different sources, including official documents and statistics, surveys, interviews, information from emblematic cases, and analysis of existing laws and regulations.
The indicators were developed over several months in a process that included an extensive review of international standards and consultation with experts. The eight areas analyzed by the Monitor include:



